Exactly 100 hundred years ago from today, on the 25 November 1915, Einstein published a paper entitled The field equations of gravitation. This paper was responsible for introducing his field theories in the form of General Relativity. Since its conception, Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity has been excruciatingly tested for flaws – of which none have come to fruition. The theory has passed every single test which has been thrown at it. But it is not completely out of the woods yet, for their is one last prediction General Relativity makes which has evaded for decades – gravitational waves.
To celebrate the centenary of advancements Einstein’s greatest theory has offered, I will take you through a brief history of how it all started as well as some of the aches and pains plaguing the theory, some of which perplexed even Einstein himself.
— Special Relativity–
During Einstein’s free time working at the Swiss patent office, he was able to daydream about what it would be like to ride alongside a light beam. Einstein’s thought experiments led to his 1905 ‘miracle year’, where he would go on to publish 4 amazing papers. Amongst proving that light exists as a particle (the photon), providing clear evidence for the existence of atoms through Brownian motion, as well as a paper on his most famous equation E = mc2, Einstein postulated a very radical theory – a theory known as the Special Theory of Relativity.
The notion of relativity has been explored since the times of Galileo. Before Einstein transformed the landscape, Newton and Galileo before him had proposed a common sense view of space and time. That was, that time was absolute and separate from space. This means that an event which takes place at a particular time, say the turning on of a light bulb inside a moving train, occurs at the same time for a person observing the light bulb who is on the train as well as for a person who is on the platform watching the train power by.
Einstein’s little thought experiment however shook this idea to its very core. If the train were to (hypothetically) be moving at the speed of light, then something very strange would happen. Ask yourself, if you were on a train moving at the speed of light and held up a mirror in front of your face, would you see your reflection?
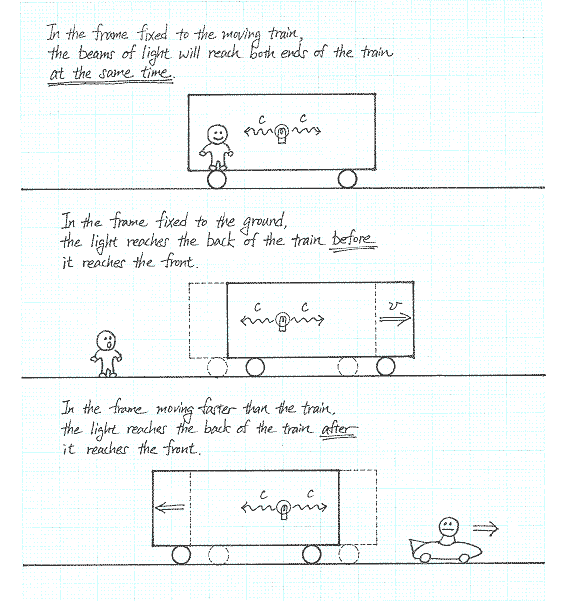
The answer is YES. This flash of inspiration came from a discovery made by James Clerk Maxwell in 1865, which was that the speed of light was constant (moving at 300,000 km/s). If the speed of light were to remain constant in any frame of reference (whether that be a stationary frame such as the man on the platform or a frame moving at some constant velocity such as that of the train passenger), then Einstein realised that the faster you move through space the slower you must move through time.
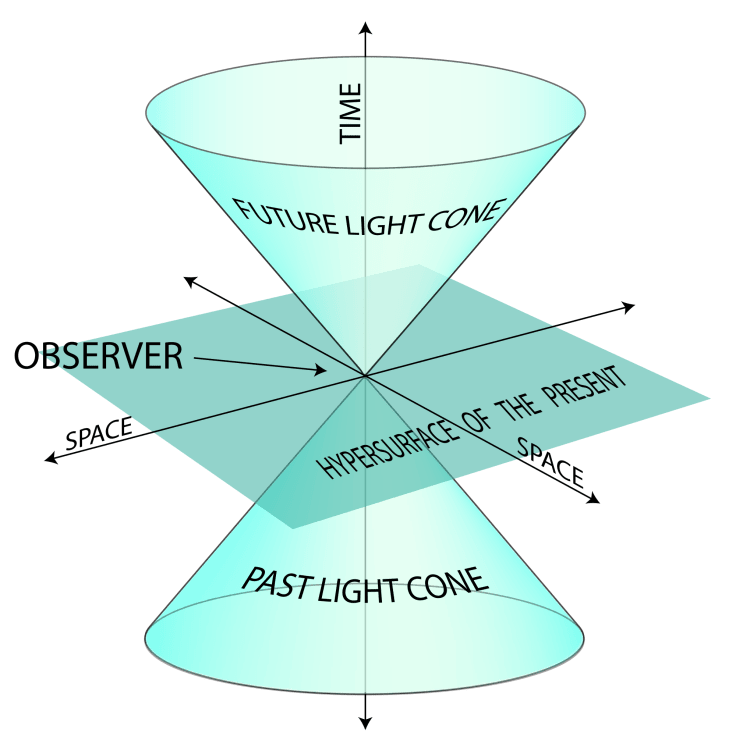
This radical idea married the ideas of time and space into a single four dimensional ‘space-time’, with the consequences involving time dilation and length contraction. This also meant that events no longer needed to happen simultaneously for observers in alternate frame of reference. One persons past could be another’s future.
— General Relativity —

Despite Einstein’s earlier successes, he realised that Special Relativity only applied to non-accelerating frames of reference. He knew that in order to correct for this he had to incorporate gravity in – the only problem was that he didn’t know how.
“In all my life I have laboured not nearly as hard; compared with this problem, the original relativity is child’s play”. – Einstein
200 Years prior, Sir Isaac Newton had been sitting outside his lodge when he saw an apple fall from its tree. This led him to formulate his law of gravity – an objects falls towards the Earth because there exists a mysterious force pulling it down. However even Newton himself was not satisfied with this explanation – objects move because they are pushed, not because they are pulled. Einstein also knew that Newton’s theory couldn’t be right and he decided to devote the next decade of his life to solving the mystery surrounding gravity.

Einstein had no idea of where to even begin. The problem had no clear boundaries. But as always, Einstein placed his faith into his thought experiments. Sitting at his office in Bern, he began to imagine what a person would feel if they were to fall off of a roof. That is when it hit him, a flash of inspiration for the ages. If you were in an elevator at the top floor, you would feel your weight as you would normally do so on the ground. This is because gravity is pulling you towards the centre of the Earth whereas the Elevator is being held up by a series of large cables. Now if those cables were to suddenly disappear, you would have a very big problem. The elevator would not begin falling towards the ground at the same rate as you would at 9.8 m/s2. However this is where Einstein’s inspiration kicked in – as you fell with the elevator, you would be weightless! It would be as though gravity had been switched off. So what is really going on here?

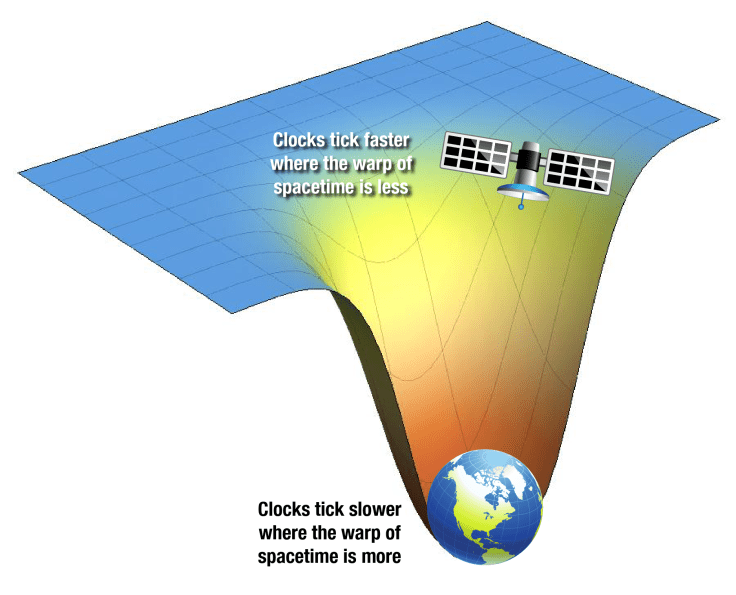
The Earth has curved the space around it, and it is the space which is pushing things downwards. Not only that, but it is space-time which is curved, so that the curvature of space also means we have some warping of time. One way to visualise this is to imagine placing a bowling ball on a trampoline. In this case we can treat the bowling ball as our Sun and the trampoline as space*. The bowling ball will sink the trampoline at its location, which directly translates to the gravitational well that is produced by any sort of mass residing in the space-time continuum. Throwing a marble onto the trampoline with some velocity parallel to the sinking of the trampoline will cause it to roll around the bowling ball – in other words the Earth in orbit around the Sun.

In essence, anything with mass or energy warps space-time, creating a gravitational field.
*The catch here is that the trampoline representation is one spacial dimension smaller than our space-time reality. This means for an accurate representation you would have to imagine a bowling ball inside a three-dimensional trampoline. If you’re having trouble visualising this don’t fret, the top scientists are in the same position as you are!
— Confirming General Relativity —
Just prior to publishing his theory, Einstein used a long known problem regarding the orbit of mercury to self-check General Relativity. At that point, it had been known for quite a while that Mercury’s orbit around the Sun deviates from Newton’s Laws of Motion. Rather than having an elliptical orbit around the Sun, it tilts a little which causes it to trace out an orbit reminisce of the petals of a flower. After painstakingly calculating the orbit of Mercury using his own General Theory of Relativity, he observes a near perfect match.

The first confirmation came in 1919. One of the predictions which arose from General Theory was that a gravitational field bends passing light rays, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. This provided the perfect way to test his theory – light coming in from stars in a distant galaxy would be bent as it travels passed the curved space around our Sun. The problem then becomes how to see this light when the Sun produces its own blinding light via the processes of nuclear fusion. Fortunately for Einstein, this problem is solved momentarily during a total solar eclipse.

“Light only knows straight lines – what’s bent is space.” – Neil deGrasse Tyson
British Astronomer Sir Arthur Eddington succeeded in photographing the Hyades star cluster which was visible during the total solar eclipse. The relative position of the stars was compared to how they looked several months before (where they were well out of the Sun’s path) and what they observed was a bending by the amount Einstein had predicted!
It took almost half a century for the next crucial verification of Einstein’s theory. General Relativity predicted that radiation (including light) would become stretched in a gravitational field – an effect known as ‘gravitational redshift’. It was at Harvard University where physicists placed a radioactive source in the basement of a tall building with a detector on the roof. The idea was that due to the difference in gravity at the top and bottom of the building would reveal this gravitational redshift. After taking measurements, they flipped the experiment so that the source was on the roof and the detector in the basement. Just as expected, the radiation that came from the basement had a wavelength that was slightly longer than that emitted from the roof. Gravity had stretched the electromagnetic waves.

One final verification came when dealing with the time aspect of space-time. Not only was spaced altered, but time itself was also stretched in a gravitational field. This indicated that the further inside a gravitational well you are (or more simply closer to Earth’s surface), then the slower time ticks for you. This was none more apparent when engineers launched satellites for our Global Positioning System (GPS) devices to work. Initially the engineers who launched these satellites didn’t believe in the non-sense that is time dilation, yet after a couple of hours in orbit our navigations systems were offset by a number of kilometres. Luckily they were able to correct for this effect as they had taken measures ‘just in case’ Einstein was right. Seems like they should have had a little more faith in him!
— Problems in General Relativity —
Despite all of its successes, there are still a couple of major issues surrounding General Relativity.
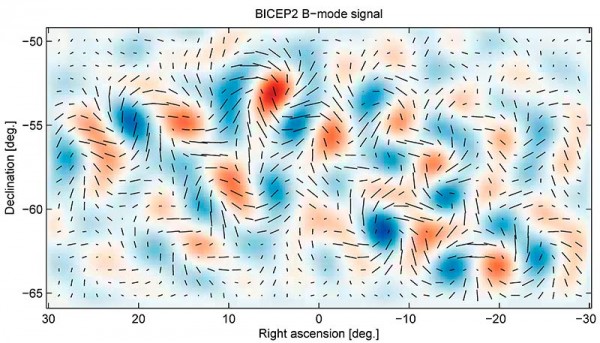
The last piece in completing the General theory of Relativity lies in finding gravitational waves. Einstein predicted that when any sufficiently large scale masses are accelerated then little ripples in space-time should radiate outwards. However Einstein predicted that even the most calamitous events in the cosmic realm would produce only the feeblest of waves. While we haven’t detected gravitational waves yet*, there is speculation that pulsars (rotating neutron stars) could hold the key. Except for black holes, neutron stars are the densest objects in the cosmos. The gravity on its surface would be about 1011 times the strength than what we experience here on Earth, with a teaspoon of the stuff weighing in at about a billion tonnes. If a pulsar happened to link up with an ordinary star, then in theory their oscillations should emit disturbances in the form of radioactive waves.
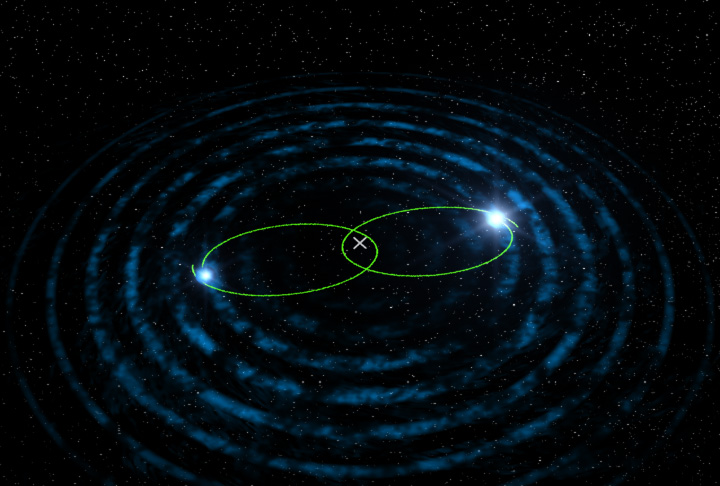
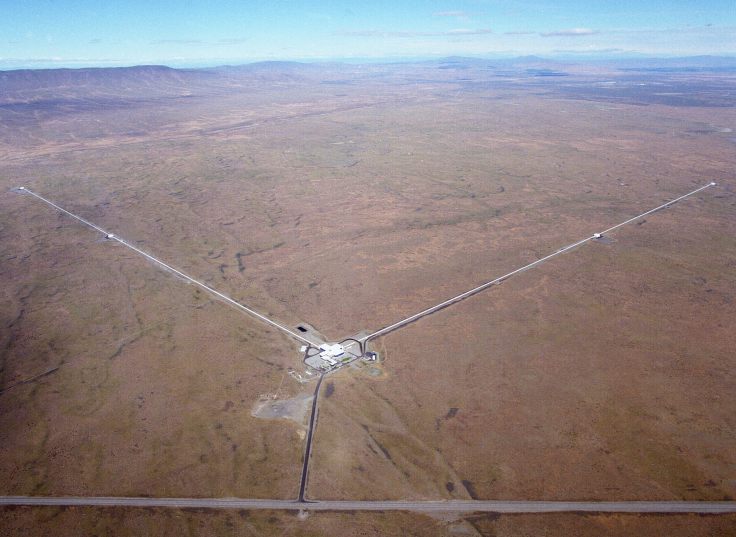
The only worry at this stage is with how to detect these tiny waves. Several detectors have been built around the world, with the most notable being the Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory, or LIGO for short. LIGO consists of two large L shaped detectors which pick up small disturbances via a method of laser interferometry. Two sets of these detectors are crucial to verify that the source is indeed a gravitational wave and not a rogue signal, such as the rumble of a truck in the distance. As you would imagine they are extremely sensitive, with upgrades in progress to increase the sensitivity 10-fold.

*The big stir caused by the BICEP2 data taken in the Antarctic last year turned out to be a false flag. What looked to match the expected signals for gravitational waves was actually the signals due to cosmic dust which was not accounted for, as verified by the Planck data.
The final issue with General Relativity is its refusal to talk with Quantum Mechanics. Einstein himself wrestled with the idea of merging the two theories but was unsuccessful. Quantum mechanics basically deals with quantised energies – that is, small packets of energy in the form of photons or other ‘messenger’ particles. In order to complete the standard model of particle physics, physicists are searching far and wide for the hypothesised messenger particle of gravity – the graviton. Many believe that if the graviton is discovered, then a grand unification theory may actually be possible – something that Einstein had been working on up until his death in 1955.
— Something Extra —
One of the more exotic predictions from General Relativity was the existence of an object so dense that it curved space-time to the point where it became isolated from the rest of the universe. Black holes warp the space-time around them to such an extent that at its centre, the singularity, the equations governing space and time break down. The results which yield infinite density and time dilation indicates that the General theory of Relativity is incomplete.

If you have seen the film Interstellar then you may have some notion of what happened towards the end of the film where they went into orbit around the black hole, Gargantua. When Cooper refers to the Quantum data inside the black hole, he is specifically referring to the data that will help reconcile General Relativity with Quantum Mechanics. Additionally it explores the idea that time ticks more slowly in regions of very high gravitational fields (or more explicitly the greater warping of space-time) when they visit Miller’s planet and go into orbit around Gargantua.





Accelerated motion & light
On the moon’s surface, a passenger car is accelerating to the right. A starlight (horizontal) is passing through a hole A in the front wall, and reaches B in the rear wall of the passenger car. Frequencies of A and B will be the same. Therefore, number of waves existing between A and B will be constant (even at different accelerations). Above is not only for uniform acceleration but also for non-uniform acceleration.
On the moon’s surface, a passenger car is accelerating to the right. A light emitted from light source A’ in the front wall reaches B in the rear wall. What is frequency of A’B ? How many waves exist between A’B ?
LikeLike
Bending of light (by gravity)
Light will not be bent by gravity. Because…
1) At the center of Milky Way galaxy (where we live), it’s said that a black hole exists. Around it, several stars are revolving. These orbits seem to be natural.
2) How about a star, before it is occulted by the moon or Jupiter ?
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury (an essay)
Perihelion shift of Mercury is about 574 arcsec per century, and main cause is said to be perturbations due to the gravity of other planets (Venus is about 280 arcsec, Jupiter is about 150 arcsec).
There is a question. At the left end and the right end of the orbit of Mercury (a view from above), force that accelerates and decelerates Mercury by perturbation by other planets will be equal (in probability). Especially in the span of the century. Main cause will not be gravity of other planets.
P.S. Perturbations of other planets will be caused only by the position of these on the orbits (and speed of gravity will be infinite).
LikeLike
Aberration on the moon
Many of widely accepted explanations for aberration will be right if these are on the moon. Illustration of raindrops and an umbrella will be OK. But as already mentioned, aberration on the earth is completed in the upper atmosphere. The explanation for aberration of earth must be rewritten.
Aberration (both on the moon and on the earth) is incompatible with constançy of the speed of light, and existence of aether is a prerequisite.
LikeLike
Notices on anti-relativity
Shown below (notices are mine, selected) will be plain and definite (sorry, in English are 5 and in Japanese are 34 notices).
http://www.asyura.com/0306/idletalk2/msg/1242.html2
LikeLike
Inertial force is not fictitious
On a plane (without friction), a body is pulled to the left by two strings and to the right by one string. The tension of each string is the same F. That is, the body is accelerating to the left. Inertial force is not fictitious (Newton’s third law of motion holds at the left end of the body).
LikeLike
Time delation
A point light source is shining (frequency is constant). Two spacecrafts are moving away from the light source in opposite directions at the same speed (three are on a straight line). Two spacecrafts are receiving light of the same frequency. There is no time delation.
LikeLike
Gravitational time dilation
Laser beam (frequency is constant) emitted from the ground is reflected by the mirror at the top of the high tower, and returned to the ground. Frequency at these three points is the same. There is no time dilation.
LikeLike
Acceleration and non-acceleration
A passenger car is moving in a uniform accelerated motion to the right. In the car, a ray of light emitted downward from the roof will be bent to the left (as a parabola). Defference of acceleration and non-acceleration is not relative (but absolute).
LikeLike
Acceleration and non-acceleration
A passenger car is accelerating to the right. In the car, lights (frequency is constant) are emitted from light source settled on rear and front walls, and at the center of the car, interference fringes are observed. Varying of interference fringes will reflect varying of acceleration. Sagnac effect like will also occur in a straight line.
LikeLike
About light (re-post)
◎ How are light waves propagated ?
1) Emission theory (for a few seconds only)
2) On aether (after the above)
◎ How are light sources visible ?
1) For celestial bodies beyond a few light-years, effect of emission theory is too small to be found (e.g. binary stars). So, every celestial body is visible to be stationary on aether (celestial sphere). Also by various aberrations.
2) Moon is by emission theory.
3) Celestial bodies in solar system (excluding moon) are depending on planetary aberrations. Also, depending on other aberrations (but, is secular aberration offset ?).
◎ Motion of light relative to observers
Same as bodies. Follows Galilean transformation. Constancy of speed of light cannot be hypothesized. By the way, light waves (speed = fλ) and photons (rays) are basically different. Especially in outer space.
LikeLike
Acceleration and non-acceleration
A passenger car is moving in an accelerated motion to the right. A light source is set at rear of the car and a measurement device is at front. The number of light waves in the car will be higher than before accelerating. The difference between acceleration and non-acceleration will be physical difference.
P.S. Inside of the car is vacuum.
LikeLike
Speed of light
In outer space, plane waves of starlight are coming from just above. A spacecraft is sailing horizontally. What should we think of speed of the spacecraft relative to light waves (c=fλ) and relative to photons (light rays)?
LikeLike
Speed of light (an essay)
The defined value of speed of light is based on measurements (with wavelength and frequency) done by Evenson et al. in 1973. Error is 1.1 m / s in pramai. Now measuring instrument is separated into a measuring part and a light source part. When one of them is moved at a constant speed higher than above error (in the direction of light path), different value will be obtained.
LikeLike
Free fall (an essay)
Rewriting of my past post (Sep 7 2021)
An elevator cabin is falling in free fall. Cabin is made up of n mass points (with the same mass of m). Imagine a single moment of falling.
Inertial force acting on each mass point is the same ma. No exceptions. On the other hand, magnitude of gravity acting on each mass point is not the same slightly. Difference depends on the position of the mass point.
P.S. For the entire cabin, magnitude of inertial force and gravity is equal.
LikeLike
Lorentz contraction
Plane waves of starlight (wavelength is constant) is arriving from upper left 45 degrees. Two spacecrafts are sailing in the right and left directions. Number of waves hitting the front and rear ends (A and B) of each spacecraft is the same. Therefore, number of waves existing between A and B is invariant (for both spacecrafts, regardless of lateral motion). Lorentz contractions will be impossible.
Relativity of simultaneity will be impossible also.
LikeLike
Free fall (an essay)
An elevator cabin is falling in free fall. Cabin is made up of n mass points (with the same mass of m). Free fall is supposed to be a uniform acceleration.
Inertial force acting on each mass point is the same ma. No exceptions. On the other hand, magnitude of gravity acting on each mass point is not the same slightly. Difference depends on the position of the mass point.
P.S. For the entire cabin, magnitude of inertial force and gravity is equal.
LikeLike
Supplement to my post (sep 4 2021)
Even in a resultant force, inertial force is inertial force, and gravity is gravity. Vector follows own law each and is inviolable.
Cabin is made by a 3D printer. Material is uniform.
On a plane (no fliction), elevator cabin is moving in a uniformly accelerated linear motion (to the right). Inertial force acting on every local area (mass is m) of the cabin is the same ma (vector is the same also).
LikeLike
Free fall (reexamination)
Problem of free fall in an elevator will be problem of resultant force of inertial force and gravity (nothing else). In any local area, it will be so also.
Note: Inertial forces acting on every local area of the cabin (supposition: mass of every local area is m) is the same ma.
Note: External force (gravity) and inertial force acting on entire cabin are equal (Newton’s second law and third law of motion). How about in local area ? To image will not be difficult.
LikeLike
Aberration (reexamination)
Aberration is caused by various motions of Earth relative to stationary aether (uniform isotropic). Light that enters upper air of Earth (from aether) is bent in the direction of motion of Earth. As a phenomenon, aberration is completed in the upper air. The same as refraction.
Therefore, illustration of raindrops and an umbrella is NG. Result of Airy’s experiment with a water-filled telescope is only natural. It is said that apparent displacement of stars is displaced in the direction of Earth’s motion, but in fact, it will be the opposite. You can check this by drawing light bending (in upper air) on a paper.
LikeLike
Aether
Existence of aether (uniform isotropic) is precondition for Newton’s first and second laws of motion. There can be no other explanation.
LikeLike
Supplement to my post (July 10)
1) In space far from light source, propagation of light follows aether frame. See again various aberrations.
2) In space close to light source, propagation of light follows the emission theory. See again various facts.
3) In outer space, a mirror is moving at a uniform speed. Plane waves of light of a star are reflected by this mirror. 1) and 2) must be seen as facts.
LikeLike
Allow me to rewrite my post (27.April).
Constancy of speed of light (Reexamination)
Constancy of speed of light is not possible always. No, it will be
possible limitedly in the following two events only. Btw, speed of
light in mediums is not subject of this reexamination.
1) A measurement point and a light source are stationary in the same
inertial frame. Distance between the two is within a few light
seconds. Speed of light is c.
2) A measurement point is stationary in aether frame. Light
propagated in aether is coming to this point. Distance from the
light source is more than a few light sveconds. Speed of light will
not be c.
Translated with http://www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
LikeLike
Constancy of speed of light (Reexamination)
Constancy of speed of light is not possible always. No, it will be possible limitedly in the following two events only. Btw, speed of light in mediums is not subject of this reexamination.
1) A geometric point and a light source are in the same inertial frame. Distance between the two is supposed to be within a few light seconds.
2) A geometric point is stationary in aether frame. Light propagated in aether comes to this point. Distance to the light source is supposed to be more than a few light seconds.
Translated with http://www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
LikeLike
Space and time will be absolute (a supposition)
Perhaps, space and time each will be absolute. Each will not be affected by any phenomenon or situation (at all). If so, relativity is impossible.
LikeLike
Is equivalence principle true?
A disk is rotating. Tilt of axis of rotation is 45 degrees. Centrifugal force (inertial force) and gravity will be non-interfering and independent. In addition, gravity of the moon is also acting.
LikeLike
Pelihelion shift of Mercury (an essay)
Some wide binaries are separated by one light years. And many wide binaries are at most (as much as) by 1000 au. These motion will be treated as mass points (a point). On the other hand, many close binaries are found out also. What are physicists who repeat nonsense on perihelion shift of Mercury ?
LikeLike
Moon and earth (an essay)
As moon passes overhead, high tide (one of two high tides a day) will come after a short delay. But why ? Why is seawater with a low specific gravity bulged ? Newton imagined that moon will continue falling. Earth will continue falling also. And seawater will cotinue falling too. So, it doesn’t matter how specific gravity is.
LikeLike
Moon and Earth (additional)
Suppose the moon and the earth is two-body problem. And imagine, the earth is revolving (not rotating) around the common center of gravity with the moon. The orbit is a perfect circle. If lunar attractive force acting on the center of gravity of the earth is action, the centrifugal force of the earth is a reaction. And the strength of the two will be equal. This will be also true for the earth as a whole.
In an illustration, the earth is drawn next to moon. Imagine two points on the surface of the earth closest to the moon and farthest from the moon. The difference between lunar attractive force and the centrifugal force of the earth at above two points will be almost equal and therefore the resultant force will also be almost equal. This will explain that the level of high tides twice a day are almost equal.
Note: Is the law of action and reaction valid for celestial bodies on elliptical orbits?
LikeLike
Moon and earth (an essay)
In an illustration, the moon and the earth are drawn side by side. Because of the lunar attractive force, seawater is bulged in the left and right edges of the round earth. The bulge is symmetrical. Two resultant forces are acting at two edges (to the opposite direction). Two resultant forces each are composed of the lunar attractive force and the centrifugal force caused by earth’s orbital motion (moves around the common center of gravity with the moon). Two resultant forces will be equal strength. This will explain that the level of high tides twice a day are generally the same.
Also, the lunar attractive force acting on the earth’s center of gravity (not the center of mass) and the centrifugal force resulting from its orbital motion (mentioned above) will be action-reaction and will be equal.
P.S. Is action-reaction in the sky exactly equal ?
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury (rewritten)
Mercury is moving on the revolution orbit. The sun’s gravity is equal to the centrifugal force. Because the two are action and reaction. Following are some explanations. Centrifugal force follows Mercury’s mass. But in addition, gravity is affected by the size of Mercury (and acting position of gravity is different). These are caused by the non-uniformity of gravity (in the space occupied by Mercury). And after perihelion passage, orbit will be pulled inward (from its original orbit).
High tide level twice a day is the same. Gravity and centrifugal force caused by the moon will be action and reaction. Centrifugal force is not fictitious.
LikeLike
FPerihelion shift of Mercury
In Mercury, the non-uniformity of the Sun’s gravity (in the size of Mercury) will be the main cause of perihelion shift. Even in artificial satellites, the effects of non-uniformity of the Earth’s gravity (the position of the center of mass and the center of gravity are different) are also mentioned.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
“It can be safely said that gravity of other planets has no effect on the perihelion shift of Mercury”. It’s in a website.
Imagine that with long radius of orbit of Mercury, the space of the solar system is divided into left and right. The probability that other planets exist on the two is equal. There will be no shift of perihelion inu one direction at constant speed (common view is wrong).
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
The perihelion shift of the earth is 11.45 arcsec / year. Main cause will be its size (size of sphere). It is the same to Mercury. In addition, the earth has a moon as a satellite that Mercury does not have. The inertial force of the moon and gravity of the sun acting on the moon are also considerable. And like Mercury, effect of other planets must be slight and unstable.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
This is the top of tall tower. Two rods of equal mass and different length are arranged vertically (heigth of center of gravity is the same). Now, two rods start to fall at the same time. The fall of center of gravity will not be the same. Because the strength of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. This will be the main cause for perihelion shift of Mercury.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
Let’s reconsider the main cause of perihelion shift again. On Mercury or Venus, main cause will be the size of sphere. On Earth or Mars, effect of satellite is added. On asteroids each, effects of size is negligible. On Jupiter or Saturn each, the powerful and unstable effect of the other will act. On Uranus or Neptune each, slight and unstable effect of the other all planets will act. Anyway, common view on Mercury is wrong.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
There is a model of Mercury. A long lod penetrates a true sphere and at the both ends of the lod, weights are set. This model is rotating horizontally and is moving on the orbit of Mercury (two planes fall on). Main forces acting on the weights are gravity of the sun and inertial force (centrifugal force). And each force acting on the outside weight and inside weight is different.
Inertial force pulls the orbit to the outside. But actual orbit of Mercury is pulled to the inside. Gravity of the sun acting on the two weights is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (not come out even. not plus minus zero). In Mercury, the action of gravity will be superior.
A model of Mercury is shown previously. Now, there are plural models. Length of lord and mass of weight each is different. These are revoleved around separately on the real orbit of Mercury. Maybe, all will be explained by Newton’s theory (including 575 arcsec).
LikeLike
Gravity lense
Gravity lenses are said to be a positive evidence of GR. However if gravity of gravitational source can be estimated, which is real GR or Newton’s theory will be clarified.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
The value of perihelion shift of planets is constant. It will not be three problem or many body problem. And it will be the same to binary star.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
Perihelion shift moves forward constantly. It cannot be explained by gravity of other planets.
On asteroids, no perihelion shift will be observed. Some size is needed.
Cause of perigee movement of the moon is written to be the sun. Not consistent. Because it will be the same phenomenon to perihelion shift of planets.
LikeLike
Perihelion shift of Mercury
Mercury revolving is divided in two (in hemisphere A facing the sun and the other B). Inertial force is A<B and gravity is A>B.
Above must be the most natural explanation of perihelion shift of Mercury. Because the value of perigee movement of the moon is remarkable (around 8.85 years). On the other hand, value of asteroids will not be found. Common explanation (main cause is other planets) is not acceptable.
LikeLike
Equivalence principle
Difference between acceleration and nonacceleration seems to be more basic. If so, equivalence principle is invalid.m
LikeLike
Sagnac effect
Sagnac effect will be explicable by Ritz’s emission theory. There is a light path of an equilateral triangle (formed by a light source and two mirrors). Three apices is three emission points and can be regarded as three inertial frames (inertial frame at the moment of emission).
Is a light source accelerating or not ? Fundamentally, it will be impossible to know.
LikeLike
About inertial force (I say again)
On a plane, there are two passenger cars. One is accelerating and the other is at a standstill. Difference of the motion of the two is not relative but absolute.
On a plane, a passenger car is accelerating. On the floor (no friction), a body is put. This body is not accelerated (to everyone). Frome physics of 20th century, nonsenses overflow.
LikeLike
Aether
Speed of light relative to mediums (water or air) is constant. Speed of light relative to aether (physical substance) is constant also. Aberrations show that.
LikeLike
Funny fact.
I recently discoverd Einstein dit not invent the relativity theory. He transformed the narative into mathematics, but the imagination of the narative goes much deeper into the Zeitgeist …. I discoverd it by telling my kid about Jules Verne “80 days around the world”, realiziing the story explains relativity pefetly and next wondering what the relation was with Einstein. .. Did you know little Einstein got “saved” out of social-locked-in problem by the stories of Jules Verne?
LikeLike
Inertial force
On a slope (no friction), a body m is sliding down. Action of gravity is mg. Then, how about the reaction ? It is resolved to two vectors. Inertial force is not fictitious.
LikeLike
Free fall
Every inertial force is measurable. Every gravitational force is measurable also. Principally. In an elevator in free fall, there is no exception.
LikeLike
Gravitational Redshift
Some books (e.g. Einstein’s Legacy by J Schwinger) say, “Frequency of a light source that is at a standstill in a different gravitational field and frequency that an observer receives is the same. But it is not the same with frequency that the same source at hand (of the observer) emits” (gist). True or not will be proved easily by interference of this two lights (by earthly experiment).
A light path forms a long oblong. From an apex of the oblong, light (frequency is constant) is being sent and returns (only a round : clockwise). Short two light paths (horizontal) are in different gravitational field. Frequency at four apexes is the same.
Sorry, I cannot receive E mail. I do not have PC.
http://www.geocities.co.jp/Technopolis/2561/eng.html
LikeLike